Complete Step-by-Step Guide to Fix chrome-error://chromewebdata/#
Step-by-step fixes for chrome-error://chromewebdata/# covering browsing, debugging, and embedded browsers with commands and config examples.
Feb 21, 2026
Master five quick Inspector, Console, extension, and userscript tricks to bypass website scroll locks instantly.
Have you ever landed on a page where you can’t scroll—trapped by a pop‑up, a paywall prompt, or a single‑page layout? Whether you’re a non‑technical user, a QA tester, or an accessibility advocate, your browser’s Developer Tools (Inspect Element, usually opened with F12) can break you free. Below is a step‑by‑step guide that walks you through quick one‑offs, scenario‑specific fixes, and permanent, automated solutions.
Beginners who need a fast, manual fix without installing anything.
Intermediate users seeking reusable Console snippets.
Developers/QA testers wanting persistent scripts or CI‑friendly workflows.
Accessibility advocates ensuring every user can navigate properly.
Websites lock scrolling for various reasons:
Pop-ups & Modals: Force your attention on ads or subscription prompts.
Single-Page Layouts: Designers limit scroll until animations or transitions finish.
Paywalls & Prompts: News sites (e.g., The New York Times) disable scroll to drive subscriptions.
Custom Code: CSS (overflow: hidden) or JavaScript event listeners intentionally block scroll.
Understanding the “why” helps you choose the most effective fix below.
| Method | Who it’s for | When to Choose |
| Inspector CSS Override | Absolute beginners needing a one-off fix without installing anything. | Fastest ad‑hoc remedy—use when you just need to scroll once. |
| Console Snippet | Keyboard-friendly users who don’t mind pasting a bit of JavaScript. | Use when you prefer code over clicking through styles. |
| Scenario-Specific Tips | Users who know precisely what’s blocking scroll (modals, paywalls, headers). | Jump here after identifying your particular obstacle. |
| Browser Extensions | Non-technical or casual users wanting a click-and-go solution. | Choose for persistent, zero-config fixes via your browser’s store. |
| Persistent Userscript | Power users, developers, or QA teams conducting repeated tests. | Opt for a permanent, cross-site automation of scroll fixes. |
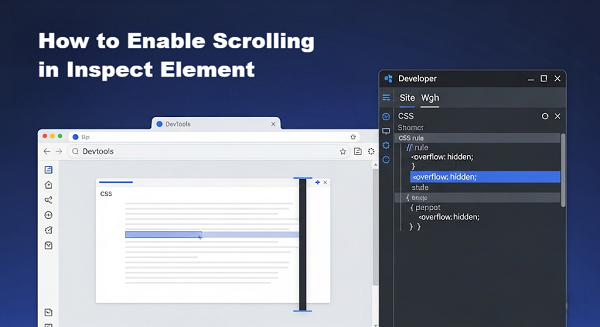
This method uses your browser’s developer tools to tweak CSS and unlock scrolling.
Press F12 (or Ctrl+Shift+I on Windows, Cmd+Option+I on Mac).
You’ll see the page’s HTML structure on the left and CSS rules on the right. If you don’t see CSS rules, click the Styles tab on the right.
Click the <body> element in the DOM tree.
In the Styles pane, look for:
css
overflow: hidden;
height: 100vh;
max-height: 100%;
position: fixed;
Uncheck each offending rule to gray it out, or Double-click the value (hidden) and replace it with auto.
Scroll or drag the scrollbar—if it works, you’re done!
Pro Tip: If the page still won’t scroll, use the Select Element tool (magnifying-glass icon) to click the locked region. Inspect parent <div>s for the same CSS and disable them too.
To override scroll restrictions instantly.
Press F12 → Console tab.
One or more of these commands:
js
// CSS override
document.body.style.overflow = 'auto';
document.documentElement.style.overflow = 'auto';
// Remove JS scroll‑lock listeners
document.body.onscroll = null;
document.body.onwheel = null;
window.onscroll = null;
window.onwheel = null;
Attempt to scroll. If it still won’t move, try the next snippet.
Save frequently used snippets in the DevTools Snippets panel for one-click execution on any page
If you see “undefined,” run commands one at a time and check for typos.
Apply the method that fits your exact situation:
| Scenario | Solution |
| Pop-up Ads / Modals |
Inspect the modal’s <div>, disable its overflow: hidden, or add to Styles pane: .modal-open { overflow: visible !important; } |
| Single-Page Layouts |
In Console: document.documentElement.style.height = 'auto'; |
| Sticky Headers / Fixed Elements | In Inspector, disable position: fixed on the header container. |
| Social Media Pages |
Run: document.body.onscroll = null; |
| Subscription Paywalls | Note: CSS/JS tricks usually won’t bypass server-side paywalls. Consider legitimate access or alternative sources. |
Extensions automatically unlock scrolling with zero effort.
Force Scroll (Chrome) – Search “Force Scroll” in the Chrome Web Store.
ScrollForce (Firefox) – Search “ScrollForce” in Add-ons.
uBlock Origin / AdBlock Plus – Use the element picker to block overlay selectors.
Use Force Scroll/ScrollForce for broad CSS/JS unlocks.
Use ad-blockers when overlays (e.g., full-page pop-ups) are the culprit.
Userscripts automate scroll fixes, running every time you visit a problematic page.
From Chrome Web Store / Firefox Add-ons.
With code:
```js
// ==UserScript==
// @name Enable Scrolling Everywhere
// @match *://*/*
// @grant none
// ==/UserScript==
(function() {
const fixScroll = () => {
document.body.style.overflow = 'auto';
document.documentElement.style.overflow = 'auto';
document.body.onscroll = document.body.onwheel =
window.onscroll = window.onwheel = null;
};
window.addEventListener('load', fixScroll);
new MutationObserver(fixScroll).observe(document, {
childList: true,
subtree: true
});
})();
Every site you visit will have scrolling restored automatically.
Handles dynamic pop-ups or content injected after initial page load that would otherwise re-lock scroll.
Best for: Professionals debugging nested scroll containers (Chrome v130+).
Spot scrollable elements quickly with this built-in feature.
1. Open Elements Panel in DevTools.
2. Look for a small scroll icon next to elements with overflow.
3. Hover the badge to highlight exactly which container is scrollable.
Use Case: When CSS/Console fixes don’t reveal the scrollbar, the Scroll Badge pinpoints hidden containers you need to target.
For QA teams or power users integrating into automated pipelines:
In uBlock Origin, add domain-specific rules to hide known overlay classes.
Create a lightweight Chrome extension that injects your CSS/JS at document_start.
Save the following as a bookmark URL and click it on any page:
js
javascript:(function(){
document.body.style.overflow='auto';
document.documentElement.style.overflow='auto';
document.body.onscroll=document.body.onwheel=window.onscroll=window.onwheel=null;
})();
1. Script in CI: Store your userscript in your repository and deploy via remote config in CI (e.g., Jenkins or GitLab) to ensure QA servers always have scroll fixes applied in tests.
2. Team Sharing: Export your Tampermonkey script as a .user.js file and share via internal wiki or package manager (npm) for easy installation by colleagues.
3. Version Control: Track your script’s changes in Git to roll back or branch for site-specific customizations.
Ethical Reminder: Respect site terms of service, especially when dealing with paywalled or subscription-based content
No—CSS/JS overrides can’t fetch content behind server-side restrictions.
All changes are client-side and safe; you can always refresh to restore original behavior.
Yes—adjust the @match pattern in your userscript or use site-specific extension rules.
No—since edits run in your local browser only, they won’t break site servers or other users’ experiences.
With these five methods—ranging from one-click overrides to fully automated CI-integrated workflows—you’ll never be blocked by scroll-locking again. Try them on your next locked page and enjoy barrier-free browsing!
< Previous
Next >
 Cancel anytime
Cancel anytime No credit card required
No credit card required